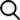
Why Choose POURLEROI as Your Powder Core Manufacturer?
With over 15 years of experience in soft magnetic materials manufacturing, POURLEROI is a trusted powder core supplier serving global clients across renewable energy, power electronics, telecom, and industrial automation sectors.
We offer full OEM/ODM customization, fast prototyping, and scalable mass production with comprehensive engineering support—from material selection to magnetic circuit optimization.
All powder cores undergo rigorous quality inspection, AL value control, and thermal stability testing to ensure consistent performance and compliance with international safety standards.
Choosing POURLEROI means securing a reliable, efficient, and customized magnetic solution for your next-generation power applications.
POURLEROI powder cores are engineered to meet the demands of system integrators, OEMs, and industrial equipment manufacturers who require reliable magnetic components for large-scale and high-efficiency power systems. In renewable energy fields, our cores are commonly integrated into PV inverters and energy storage converters to ensure stable performance under fluctuating load and temperature conditions. Telecom power module manufacturers rely on our cores for EMI filters and DC/DC converters that must meet strict regulatory and thermal requirements. In industrial automation, they are used in variable frequency drives (VFDs), servo motor controllers, and switching power supplies where stable inductance and high DC bias tolerance are essential. For automotive tier-1 suppliers, our powder cores support onboard charger (OBC) and battery management applications by offering minimal core loss and compact footprint. With consistent AL values, wide material selection, and global compliance, POURLEROI powder cores are trusted by engineering teams who need dependable, scalable magnetic solutions in time-sensitive projects.