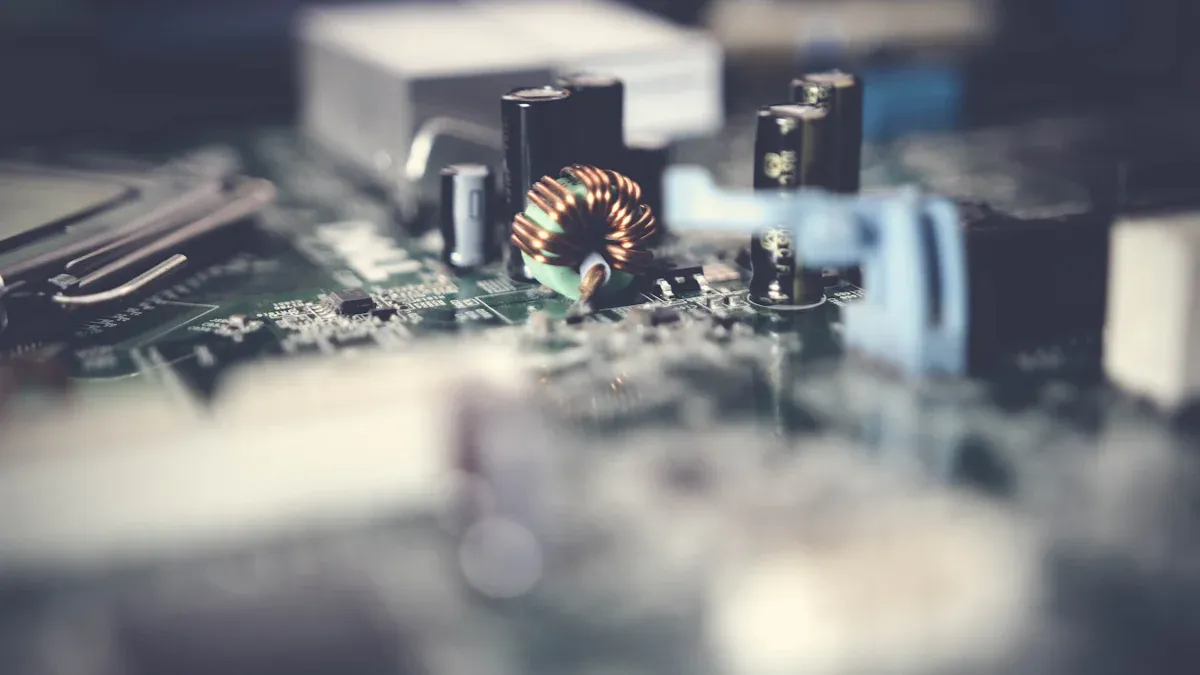
When comparing a c core transformer vs toroidal, there are clear differences in their operation and performance. Toroidal transformers generally offer better efficiency and waste less energy. They run cooler and take up less space than c core transformers. Additionally, toroidal transformers produce less electromagnetic interference (EMI), which is a significant advantage. On the other hand, c core transformers are simpler to construct and repair. Choosing between a c core transformer vs toroidal depends on your priorities, such as efficiency, size, heat dissipation, EMI levels, and ease of construction.
Efficiency: Toroidal transformers perform better
Size: Toroidal transformers are more compact
Heat: Toroidal transformers run cooler
EMI: Toroidal transformers generate less interference
Construction: C core transformers are easier to build and fix
Toroidal transformers work better, stay cooler, and use less energy than C core transformers.
Toroidal transformers are smaller and lighter. They make less electromagnetic interference. This makes them good for small spaces and sensitive electronics.
C core transformers are easier and cheaper to make, put in, and fix. They are good for high-power and industrial jobs.
Picking the right transformer depends on what you need. Think about efficiency, size, noise, heat, cost, and how easy it is to take care of.
Using high-efficiency transformers like toroidal or amorphous core C core types saves energy. It lowers costs and helps the environment.
When you compare c core transformer vs toroidal, some things matter more. Engineers care about efficiency, size, heat, EMI, and how hard it is to build. These things show how well a transformer works in real life.
Tip: Pick the right transformer by matching these things to your project.
The table below shows the main differences between the two types:
|
Metric |
Toroidal Transformer |
C Core Transformer |
|---|---|---|
|
Efficiency |
Higher |
Lower |
|
Size |
Smaller |
Larger |
|
Weight |
Lighter |
Heavier |
|
Heat Generation |
Less |
More |
|
EMI |
Lower |
Higher |
|
Noise |
Less |
More |
|
Construction Complexity |
More complex |
Easier |
Toroidal transformers have a ring-shaped core. This shape keeps magnetic fields inside better and lowers EMI. C core transformers have open ends and air gaps. This makes more flux leak out and raises EMI. Toroidal cores let wires wrap tightly, which makes them stronger and quieter.
Transformer efficiency depends on copper and iron losses. Copper loss happens because wires resist electricity. Iron loss comes from the core and magnetic force. If the temperature goes up by 40°C, copper loss can rise by 15%. This can make efficiency drop by 1-2%. Using special core materials, like amorphous alloys, can cut iron loss by 70%. This helps efficiency go up by 1-2%.
Toroidal transformers are very efficient. Their shape cuts down copper and iron losses. The wires wrap evenly around the core, so there is less resistance and heat. C core transformers lose more energy because of their open shape. They also need extra shielding to control EMI.
Voltage regulation shows how well a transformer keeps voltage steady. Toroidal transformers do this well because their core lets wires wrap tightly. There are few air gaps in the core. This helps keep voltage stable when the current changes. C core transformers have open ends. They can lose more voltage when the load is heavy. Engineers pick toroidal transformers for jobs needing exact voltage, like audio amplifiers and medical devices.
Noise and vibration can bother electronics and people. Toroidal transformers make less noise and shake less. Their round core and tight wires help with this. The doughnut shape keeps the magnetic field inside. This lowers hum and buzzing sounds. C core transformers make more noise. Their core has air gaps and wires are not as even. Places like studios and hospitals need quiet equipment. A toroidal transformer helps keep things silent and working well.
Note: When comparing c core transformer vs toroidal, toroidal transformers make less electromagnetic emissions. Their shape meets strict EMI rules for military and aerospace use. The doughnut core keeps magnetic flux inside. This cancels most magnetic fields outside the coil. It means less noise gets out, so toroidal transformers work well for sensitive electronics.
Heat management is important for safety and how long a transformer lasts. Toroidal transformers stay cooler because their core works well. Tight wires mean less resistance and less heat. C core transformers are bigger and have open cores. They lose more energy as heat. This makes them hotter and may need extra cooling. Engineers use toroidal transformers in high-performance systems to keep heat low and make them last longer.
Core losses happen when the magnetic field in a transformer’s core makes heat. Engineers call these “no-load losses.” The core’s shape and material decide how much energy is wasted. In the c core transformer vs toroidal debate, toroidal transformers have a ring-shaped core. This shape keeps magnetic fields inside. It lowers leakage flux and cuts eddy current losses. Toroidal transformers often use less steel and copper. This helps the environment by needing less mining and processing.
C core transformers can use special metals called amorphous alloys. These metals can cut core losses by up to 70-80%. Less energy turns into heat, so thousands of kilowatt-hours are saved each year. Amorphous core transformers last longer and can be recycled. This helps the planet. They cost more at first, but they save energy and last longer. This makes them a smart pick for many places.
Tip: Picking a transformer with low core losses can lower your electric bill and cooling needs.
Copper losses happen when electricity moves through wires in a transformer. These are called “load losses.” The wires resist the flow, which makes heat. In the c core transformer vs toroidal comparison, toroidal transformers have tightly wound coils. This design lowers resistance and keeps copper losses small. Less heat means the transformer stays cooler and lasts longer.
C core transformers have a different winding style. Their coils are not as tight, so resistance is higher. This causes more copper losses and extra heat. Engineers must size transformers right to keep copper losses low. Running a transformer at 40–80% of its rated power helps balance core and copper losses. This makes the system work better.
Energy use depends on both core and copper losses. High-efficiency transformers waste less energy. This means lower electric bills and less cooling needed. In big buildings, these savings add up over time. Places that use toroidal transformers pay less to run them. These units waste less energy. Their small size also means less energy is needed for cooling and moving them.
C core transformers with amorphous metal cores also save energy and cut CO₂ emissions. They can lower yearly energy use by 15,000 to 30,000 kWh. They also cut carbon emissions by 10 to 20 tons per megavolt-ampere (MVA) each year. Making these cores uses less energy and makes less pollution. Both transformer types help the environment. But toroidal transformers stand out because they last long and are small.
Toroidal transformers:
Lower core and copper losses
Make less heat
Use less steel and copper
Cut transportation emissions
Help save energy by lowering electricity use
Choosing between c core transformer vs toroidal changes efficiency, costs, and the environment. High-efficiency transformers lower energy bills, need less fixing, and help protect the planet.
Engineers look at size and weight when picking transformers. Toroidal transformers are much smaller and lighter than C core transformers. They can be about half the size and weight for the same power. The ring-shaped core in toroidal transformers uses space well. This shape lets them fit into tight spots. Toroidal transformers use all of their core, so they are compact. They also have flexible shapes that fit many places. C core transformers have fixed sizes and cannot change shape. Toroidal transformers lose less energy, so they stay small and light. Because they are compact, toroidal transformers stay cooler and are easy to move.
Installing each transformer type is different. Toroidal transformers need coils wound right onto the ring core. This takes a lot of work and special machines. The winding must be careful so wires do not break. This makes building them slow and expensive. Big toroidal transformers are hard to put in place. Their windings are heavy and can break easily. Cooling is tough because heat gets trapped inside. Engineers must add extra vents to help cool them.
C core transformers have cores that open up. Coils are made first and then put on the core. This makes building them faster and easier. The open core lets air flow better, so cooling is simple. Fixing and taking care of C core transformers is easier too.
|
Aspect |
C Core Transformers |
Toroidal Transformers |
|---|---|---|
|
Manufacturing |
Simple and easy |
Hard and takes more work |
|
Installation |
Quick and simple |
Tricky and needs care |
|
Cooling |
Air moves well |
Needs extra cooling |
|
Maintenance |
Easy to fix |
Hard to fix |
Cost is important when choosing transformers. Toroidal transformers cost more to make because they need special winding and more work. Their small size and good efficiency can save money on power and shipping later. C core transformers are cheaper to build and good for making lots at once. They are a better choice when you want easy setup, simple fixing, and low starting cost.
When picking between c core and toroidal transformers, people must think about price, savings over time, and how easy they are to install.

C core transformers are good for places that need easy fixing and strong build. Power systems use these transformers because they can handle big voltages and currents. Many engineers pick C core transformers for machines in factories, large air systems, and power stations. The open core design lets people change coils fast and fix things easily. This helps keep important systems running with less waiting time.
New core materials have made C core transformers work better. Amorphous steel and nanocrystalline alloys help save energy by lowering core losses. These materials make C core transformers a smart pick for saving energy and for power grids that need to be efficient. Amorphous metal transformers are now used in new power stations and green energy places. They can handle lots of power and last a long time, so they are trusted for tough jobs.
Tip: C core transformers are best when you care about price, easy fixing, and handling lots of power.
Toroidal transformers are great where small size, high efficiency, and low EMI are needed. Many engineers use toroidal transformers for factory robots, smart machines, and new power systems. Their round core keeps magnetic fields inside, so there is less EMI and noise. This helps protect sensitive electronics and keeps signals clear.
Many new devices use toroidal transformers. Fancy audio gear, medical tools, and small gadgets use them for quiet and steady power. Factory robots and control systems use toroidal transformers because they are small and save energy. Smart power grids also use these transformers to help green energy and cut power loss.
|
Application Area |
Key Benefits |
|---|---|
|
Industrial Automation |
Small, efficient, low EMI |
|
Robotics |
Light, accurate, stays cool |
|
Medical Devices |
Quiet, safe, works well |
|
Audio Equipment |
Low noise, steady power |
|
Smart Grids |
Saves energy, less power wasted |
When choosing between c core transformer vs toroidal, engineers often go with toroidal transformers when space, saving energy, and quiet are most important.
Toroidal transformers often work better and use energy more wisely. When you look at c core transformer vs toroidal, you need to think about a few things:
What the core is made of and how it is shaped
How much room you have for the transformer
The place where the transformer will be used
How much money you can spend and if it will save money later
What the transformer must do, like how much voltage or power it needs
Every project is different. Engineers should pick the right transformer for what the project needs to get the best outcome.
Toroidal transformers have a closed-loop core. This shape keeps the magnetic field inside. It stops energy from leaking out. The wires wrap tightly around the core. This lowers resistance and makes less heat. Because of these things, toroidal transformers waste less energy and stay cooler.
C core transformers can work with high power. Their open core helps cool them down. It also makes fixing them easier. Many factories and power plants use C core transformers for big jobs.
Toroidal transformers have a ring-shaped core. This shape keeps the magnetic field inside. Not much magnetic flux gets out. This means EMI stays low. Sensitive electronics work better with less EMI.
Yes, toroidal transformers are harder to fix. Their coils are wound very tightly. Fixing or rewinding them needs special tools and skills. C core transformers are easier to open and repair.
C core transformers cost less to make. Their design is simple and quick to build. Factories can make many of them at a lower price.
By continuing to use the site you agree to our privacy policy Terms and Conditions.